- What is dividend?
- What is dividend investing?
- What is dividend yield?
- High dividend yield stocks – top 15
- Explain importance of dividend investing with examples
- Dividend investing vs mutual fund investing
Dividend investing has become a popular strategy for investors seeking steady income alongside potential capital appreciation. It’s especially attractive to long-term investors who want to grow wealth while receiving regular payouts. This article will walk you through the basics of dividends, dividend investing, and related concepts, with examples from the Indian stock market.
1. What is a Dividend?
A dividend is a portion of a company’s earnings distributed to shareholders, typically in the form of cash payments or additional shares. Companies that pay dividends are usually well-established, profitable businesses. The payout is made on a per-share basis, meaning shareholders receive a set amount of money for every share they own. Dividends are generally paid quarterly, semi-annually, or annually, depending on the company’s policy.
2. What is Dividend Investing?

Dividend investing is a strategy where investors focus on buying stocks of companies that consistently pay dividends. This approach offers two primary sources of returns:
- Regular Income: Through periodic dividend payments.
- Capital Appreciation: As the stock price appreciates over time.
Dividend investors typically target blue-chip stocks or companies with a proven track record of paying and increasing dividends. Over time, dividends can compound, leading to significant returns when reinvested in the same or other stocks. This strategy appeals to income-focused investors, such as retirees or those looking for passive income.
3. What is Dividend Yield? – Explained with Example
The dividend yield is a financial metric that tells an investor how much they are earning in dividends relative to the stock’s price. It is expressed as a percentage and is calculated using the following formula:

Example:
Suppose a company pays an annual dividend of ₹40 per share, and the current stock price is ₹800. The dividend yield would be.
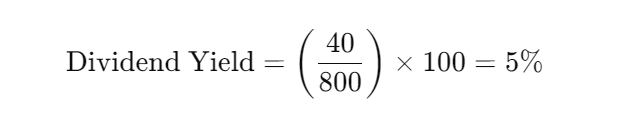
This means that for every ₹800 invested, the investor earns ₹40 per year in dividends, providing a 5% return just from dividends.
4. Top 15 High Dividend Yield Stocks in the Indian Market
Here’s a list of some high dividend yield stocks in India, based on recent data. These companies provide consistent returns to investors through dividends:
| Stock | Dividend Yield (%) |
|---|---|
| Coal India | 8-10% |
| Oil and Natural Gas Corporation (ONGC) | 6-7% |
| Power Finance Corporation (PFC) | 8-9% |
| Bharat Petroleum Corporation (BPCL) | 6-7% |
| Indian Oil Corporation (IOC) | 5-6% |
| National Aluminium Company (NALCO) | 6-7% |
| Hindustan Zinc | 7-9% |
| REC Limited | 7-8% |
| ITC Limited | 4-5% |
| GAIL India | 5-6% |
| SJVN Limited | 7-8% |
| NMDC Limited | 6-7% |
| Vedanta Limited | 7-9% |
| PTC India | 6-8% |
| Hero MotoCorp | 4-5% |
These stocks represent various sectors such as energy, mining, and finance, which typically offer high dividend yields.
5. The Importance of Dividend Investing – A 10-Year Example
Dividend investing provides a dual advantage of steady income and the potential for capital growth. Let’s consider an example where an investor bought 1,000 shares of a company at ₹500 per share 10 years ago. The company consistently pays a dividend with an 8% yield. Additionally, the stock price has doubled (100% increase) over this period.
Initial Investment:
- Number of Shares: 1,000
- Price per Share: ₹500
- Total Investment: ₹500,000
Dividend Income Over 10 Years:
- Annual Dividend = 8% of ₹500 = ₹40 per share
- Total Annual Dividend = ₹40 × 1,000 shares = ₹40,000
- Over 10 years, the total dividend income = ₹40,000 × 10 = ₹400,000
Stock Price Growth:
- Current Stock Price: ₹500 × 2 = ₹1,000
- Value of Shares Today = 1,000 shares × ₹1,000 = ₹1,000,000
Summary of Gains:
- Total Dividend Income over 10 years: ₹400,000
- Stock Value Appreciation: ₹500,000 (increase from ₹500,000 to ₹1,000,000)
- Total Gain: ₹400,000 (dividend income) + ₹500,000 (capital gain) = ₹900,000
In this scenario, the investor has almost doubled their total return through a combination of dividend payouts and stock price appreciation. This demonstrates the long-term benefits of dividend investing, where income and capital growth work together to maximize returns.
6. Dividend Investing vs. Mutual Fund Investing
Both dividend investing and mutual fund investing have their unique advantages and cater to different investor profiles.
Dividend Investing:
- Direct Stock Ownership: When you invest in dividend-paying stocks, you own shares directly in the company.
- Regular Income: Dividends provide a predictable source of cash flow, making it appealing to income-focused investors.
- Potential for Growth: High-quality dividend stocks often grow in value over time, offering the possibility of capital appreciation.
- Control: Investors can choose which stocks to buy and when to sell them, offering more control over their portfolio.
Mutual Fund Investing:
- Diversification: Mutual funds offer broad exposure to multiple stocks, bonds, or other securities, reducing the overall risk of the portfolio.
- Professional Management: Fund managers make decisions on behalf of investors, selecting securities and adjusting the portfolio as needed.
- Reinvestment: Dividends or interest from the underlying securities in mutual funds are often reinvested, which can lead to compounded growth over time.
- Less Control: Investors don’t have direct control over which individual stocks or bonds the mutual fund invests in.
Which One to Choose?
- Dividend Investing: Suitable for investors who want regular income, have the time and expertise to manage individual stock portfolios, and prefer a hands-on approach.
- Mutual Fund Investing: Ideal for investors looking for diversification and professional management without the need for direct involvement in stock selection.
Conclusion
Dividend investing is a powerful strategy for generating passive income while also benefiting from long-term capital appreciation. High dividend yield stocks in the Indian market, like Coal India and ONGC, offer attractive returns. Over time, the combination of dividend income and stock price appreciation can significantly enhance an investor’s total returns. However, choosing between dividend investing and mutual fund investing depends on your investment goals, risk tolerance, and desire for hands-on involvement in managing your portfolio.